World Tunnel Congress 2023: Tunnelling in Greece, a culture of underground activities across history
Technical and technological advancement of a society can be defined, among others, by its tunnelling projects that depict the great technical and economic power of certain civilisations. The host country of the WTC, Greece, is a shining example of ancient tunnelling and underground know-how. Innovative development that permeates the layout of cities in the country with the most recent major works of today.
Tunnelling in Greece dates back at least to 2000 B.C. when many tunnels were excavated for the exploitation of metals and minerals. Lavrion silver mines, which are located near Athens, were used during the classical era to finance the formidable navy that defeated the Persians in the naval battle of Salamis and helped flourish the Athenian Democracy of the Classical era. Other, well-known ancient mines are located in Paros, where underground marble exploitation was responsible for the extraction of the Lychnite, the famous marble of 35 mm depth transparency, that was favoured by artists such as Praxiteles’ Hermes or the unknown artist of the Venus of Milos and the Samothace’s Victory. Modern underground marble exploitation is on-going for the historical Pentelikon Marble of which the Parthenon was constructed - note that a technical visit will be available on the last day of the WTC2023, as well as in the areas of Macedonian Ancient Kingdom in Northern Greece, Drama.
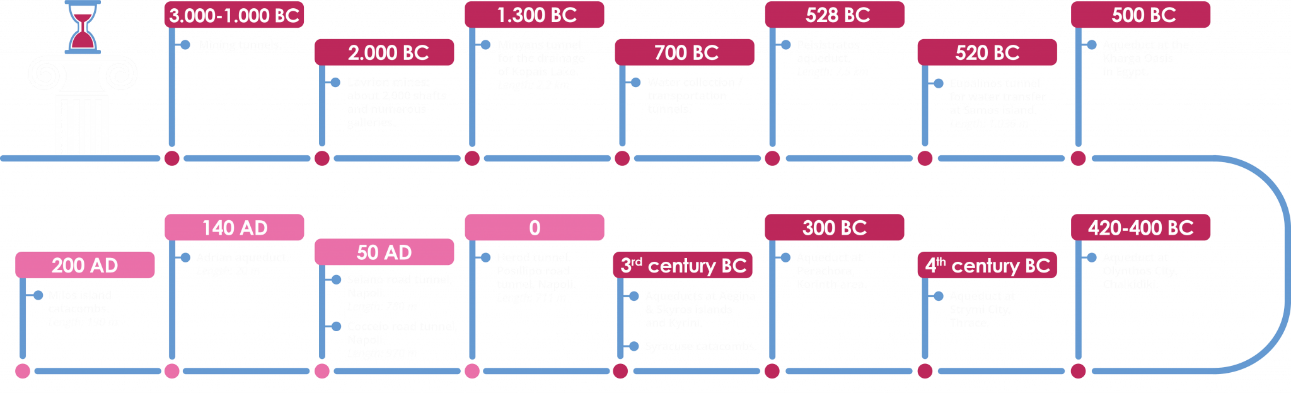
Tunnel is an engineering feat of outstanding importance since it was the first time in the history of mankind that anyone had ventured to undertake a project of that magnitude with no similar reference. The Engineer Eupalinos built a tunnel under a mountain by starting to dig, simultaneously, from two portals diametrically opposite and with the use of mathematics and geometry managed the two drives to meet halfway without any deviation.
Athens, a representative city of the expansion of the underground space
Athens is the centre of the economic, financial, industrial, political and cultural life in Greece. Its underground network has expanded considerably in recent years and this development is now accelerating significantly.
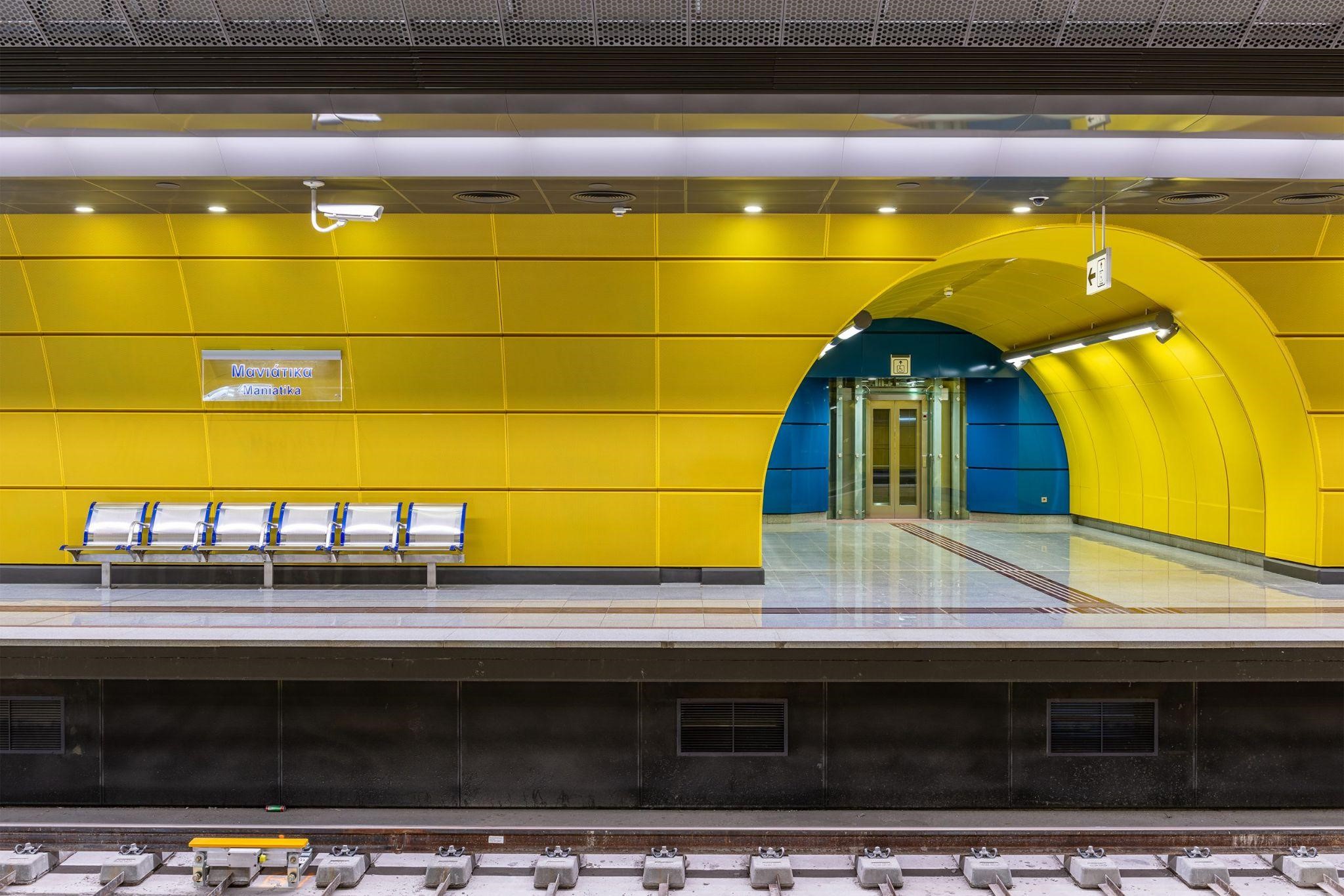
Last October the Metro Line 3 Extension Project to Piraeus was successfully completed, with the opening of the last three new stations of Maniatika, Piraeus and Dimotiko Theatro to the public. The project included a total of 7.6 km long twin-track running tunnel, 6 new modern stations and 7 ventilation shafts and is one of the most important expansions for the greater area of Athens and Piraeus in decades.
Since then, a large number of future extension projects related to the capital's Metro system have been announced: the perfect example of this expansion. A Metro network with over 110 stations in Athens is planned with 35 new stations in 9 extensions in order to create better conditions for urban transport and the connection of the Metro network in quite populated areas, the expansion of the network and the creation of new growth poles in the capital. With these extensions, Athens now aims to far exceed 100 stations on its network.
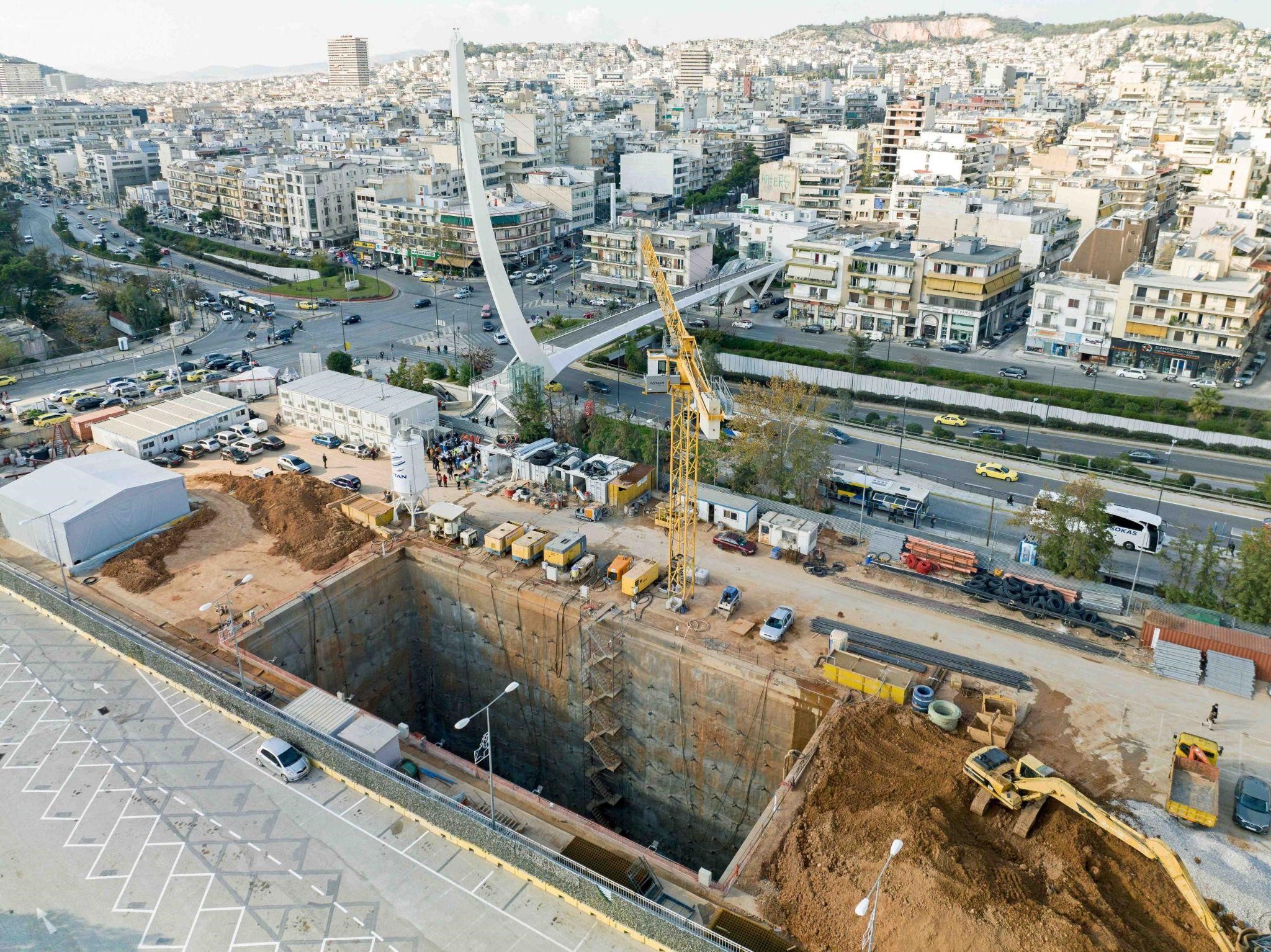

Earlier in 2022, tenders for ten new major projects were announced to be launched during the first semester of 2023 by the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport. This new package of projects, worth almost 1.6 billion euros, is added to the already swollen portfolio of large projects. Another example of the high activity related to the country's infrastructure and underground developments.
The WTC will be the occasion to visit construction sites as every year and in particular the construction sites of the new Metro Line 4. The first phase of Line 4 (from Alsos Veikou to Goudi areas) is being constructed fully underground by the joint venture “AVAX AE – GHELLA SpA – ALSTOM TRANSPORT SA” following a tender award in 2021 from the Project Owner ATTIKO METRO S.A. Among the technical challenges of this Project is TBM tunnelling under existing Metro tunnels and excavation of new stations close to operating Metro stations, whose safety and activities should remain unaffected. Furthermore, boring or digging under or next to high buildings, sometimes old or historical ones in the city center, has to be performed securing their structural and serviceability standards.
Other ongoing tunnelling projects in Greece
Thessaloniki METRO: The first Metro Line of the second largest city of Greece, Thessaloniki, is close to commencing operation in 2023. The project includes 18 underground stations, ~14.4km of tunnelling and a 50,000m2 depot area. There will be 18 fully automatic driverless and air-conditioned trains of the latest technology, as well as automatic platform screen doors in each station for improved passenger service and safety.
Northern Road Axis of Crete island: A concession project concerning the design, construction, financing, operation, maintenance of an approx. 200km long motorway which includes a significant number of tunnels with a total length over 13km. The cost of the project has been estimated at around €1.46billion euros.
Underwater road link to connect Lefkada island to mainland: To connect Lefkada island to the mainland national highways, 3.11 km roads are currently being designed of which 1.2km will be an underwater tunnel crossing the existing sea strait.
Please find more information on the website: https://wtc2023.gr/
--
About the International Tunnelling and Underground Space Association:
The International Tunnelling and Underground Space Association (ITA) is a non-profit and non-governmental international organization that aims to promote underground space's use as a solution to sustainable development. Founded in 1974 and operating out of Geneva, Switzerland, ITA currently associates with 78 Member Nations, 300 affiliated members, 14 Prime Sponsors and 60 supporters.
About the Greek Tunnelling Society:
The Greek Tunnelling Society (GTS), founded in 1995, is the established and official representative of Greece in the International Tunnelling Association (ITA-AITES). GTS is a non-profit body and aims to promote the key advantages of tunnels and underground structures from technical, environmental, social and economic point of view. The steering board of the GTS consists of 7 members, while the body of the GTS has more than 200 members. For more information on GTS, visit the official website.
